As an important basic material for modern industry, the development of aluminum profiles can be traced back to the early 20th century. In 1886, the invention of the Hall-Heroult electrolysis method made large-scale production of aluminum possible. In the 1950s, with the advancement of extrusion technology, aluminum profiles began to be widely used in the construction field. In China, the aluminum profile industry started in the 1980s, and its rapid development speed has an absolute advantage in the international market.
The rapid expansion of the industry has also brought a series of problems. Taking the construction aluminum industry as an example, the number of manufacturers in the country has increased sharply, resulting in a serious overcapacity, presenting a situation of "more porridge and fewer monks". At present, the output of most aluminum plants has failed to meet the design indicators. It is rare for companies to achieve half of the design capacity, and the market competition is extremely fierce. Although the construction industry has developed rapidly in recent years, the market demand for aluminum doors and windows is still far lower than the supply of aluminum. This imbalance between supply and demand has caused the entire industry to fall into the dilemma of "production exceeding sales"-even if the demand for aluminum doors and windows has grown rapidly, the problem of overcapacity is still prominent. Fierce market competition has spawned some undesirable phenomena. Some aluminum door and window manufacturers use all means to compete for orders. They obtain contracts through false propaganda, malicious price reduction and other means, and then use inferior products and cut corners during the construction process, in order to ensure their own profits. Consumers are reminded: Do not simply pursue low prices and ignore quality, so as not to be deceived.
Alloy elements
6063 alloy is an alloy with aluminum, magnesium and silicon as the main elements. The content of each element has strict standards. However, in order to save money, some manufacturers deliberately reduce the amount of magnesium (magnesium is expensive), even below the minimum allowable content. What's more outrageous is that some factories directly add waste wires, waste aluminum pots and other miscellaneous aluminum, resulting in the so-called "6063 alloy" not being qualified at all. Such aluminum profiles have extremely low mechanical strength and can be bent by hand. They are jokingly called "noodle aluminum" in the industry. This is why some aluminum materials on the market can be thousands of yuan cheaper - saving alloy costs and sacrificing quality! Regular large factories have their own internal formula standards, and the proportions of aluminum, magnesium and silicon are precisely controlled to ensure stable alloy performance. The "makeshift formula" of small workshops cannot be saved no matter how they are processed later.
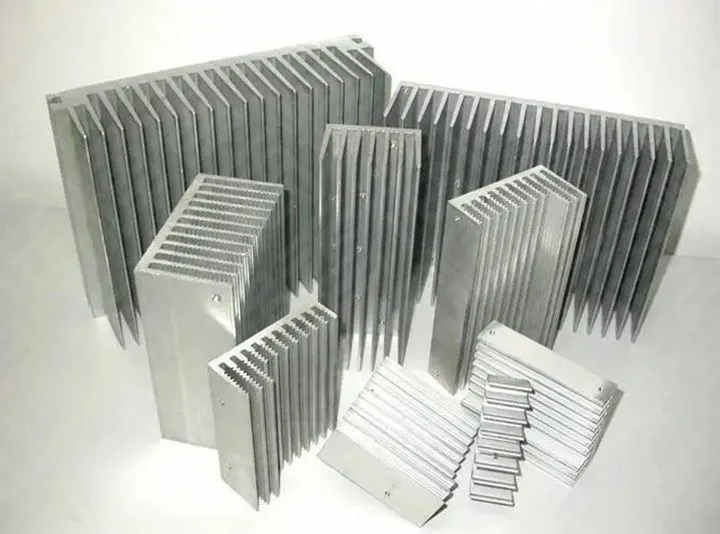
Aluminum alloy melting furnace
Aluminum alloy melting furnace equipment is crucial. The degree of advancement of the melting furnace directly affects the purity of molten aluminum. Outdated equipment will produce inferior molten aluminum. There are many kinds of furnaces used in domestic aluminum plants. The coal-fired crucible furnace (the level of the 1940s) has no chimney, and the waste gas and waste slag are all mixed in the molten aluminum. Gas or electric heating round furnace, with static furnace deslagging and degassing, the molten aluminum will be purer. There is a key problem that the furnace without a chimney will burn waste gas directly to pollute the molten aluminum. The cast aluminum rods are full of slag and bubbles, and the profiles are easy to crack and deform. The shortcomings of the static furnace will cause the aluminum water to be directly cast without purification, with many internal defects, and subsequent extrusion will inevitably cause problems. In short, inferior molten aluminum = inferior aluminum, which is also one of the "secrets to save money" for low-priced aluminum.
Alloy casting
The casting process determines the internal structure of the aluminum rod. The old-fashioned iron mold casting has coarse crystals, many slag bubbles, and a rough surface of the cast rod; horizontal continuous casting (wire rope transmission), uneven cooling, and general quality. Hydraulic semi-continuous casting (with hot top mold) is the best choice. The cast rods are finely crystallized and smooth on the surface, which is suitable for high-end profiles. Many small factories in the industry do not have the ability to cast rods. They directly purchase inferior aluminum rods from outside. The production cost is low and the price will be relatively low. This is one of the reasons for the large price difference of aluminum sales. The quality is completely out of control. The old casting equipment has low investment, but the aluminum rods produced cannot meet the standards of 6063 alloy at all. The quality of the cast rods is poor, and the extrusion equipment is useless no matter how good it is.
Profile extrusion
There are many types of profile extruders with different grades. The performance level of the extruder directly affects the quality of the final product. The simple models commonly modified from plastic extruders have problems such as insufficient precision and poor stability, which makes it difficult to control the tolerance of profile dimensions and the production quality is worrying. Taiwan-made or some domestically produced hydraulic presses basically meet conventional production needs. Professional aluminum extruders imported from Germany and Japan are equipped with precise temperature control systems and speed adjustment devices. Temperature management should be controlled in the process. The ideal extrusion temperature should be stably controlled in the range of 460-500℃. Temperature fluctuations will cause uneven material flow. The extrusion speed should be adjusted according to the complexity of the profile section, usually maintained in the range of 5-15 meters/minute. A complete cooling system needs to be equipped with multiple high-power fans (6-8 units per line are recommended) to ensure that the profile drops from 500℃ to below 200℃ within 30 seconds. Incomplete quenching will significantly reduce the yield strength of the material, and the tensile strength may be lost by 15-20% after testing. Improper extrusion process will cause defects such as surface stripes and twisting deformation of the profile, and the yield rate may drop by 30-50%. For dimensional deviations caused by insufficient equipment precision, it is recommended to focus on the brand and service life of the equipment, the configuration of the temperature control system, the completeness of the cooling system, and the daily maintenance records when purchasing. Although the investment in high-quality extrusion equipment is large, in the long run, the cost can be recovered by increasing the yield rate and reducing the scrap rate. It is recommended that enterprises with conditions give priority to it.
Comments
0